How Does a Rotary Evaporator Remove Solvent?
If you work in a lab, research facility, or industrial setting, you’ve likely heard of a rotary evaporator (or "rotovap"). This essential piece of equipment is a go-to tool for efficiently removing solvents from samples. But how exactly does it work? And why is it preferred over other solvent removal methods?
As a leading manufacturer of rotary evaporators, we’re here to break down the science, mechanics, and practical benefits of this device in simple terms. Whether you’re a lab technician, a purchasing manager, or simply curious, this guide will answer your questions and explain why rotary evaporators are a must-have for solvent removal.
What Is a Rotary Evaporator?
Let’s start with the basics. A rotary evaporator is a laboratory instrument designed to gently and efficiently remove solvents from heat-sensitive samples. It’s widely used in chemistry, pharmaceuticals, food production, and environmental testing. The key advantage? It works at lower temperatures than traditional evaporation methods, protecting delicate compounds from degradation.

But how does it achieve this? Let’s dive into the process.
The Science Behind Solvent Removal
To understand how a rotary evaporator works, we need to revisit two basic principles of chemistry: evaporation and boiling points.
Evaporation: This is the process where a liquid turns into vapor. It happens naturally at room temperature but speeds up with heat.
Boiling Point: The temperature at which a liquid boils and turns into vapor.
However, boiling points aren’t fixed—they change with pressure. Lower the pressure (create a vacuum), and the boiling point drops. This is why water boils at 100°C at sea level but at lower temperatures on a mountain.
A rotary evaporator uses this principle to remove solvents without overheating the sample. Here’s how:
Step-by-Step: How a Rotary Evaporator Works
Let’s break down the process into simple steps:
1. Rotation: Spreading the Sample Thin
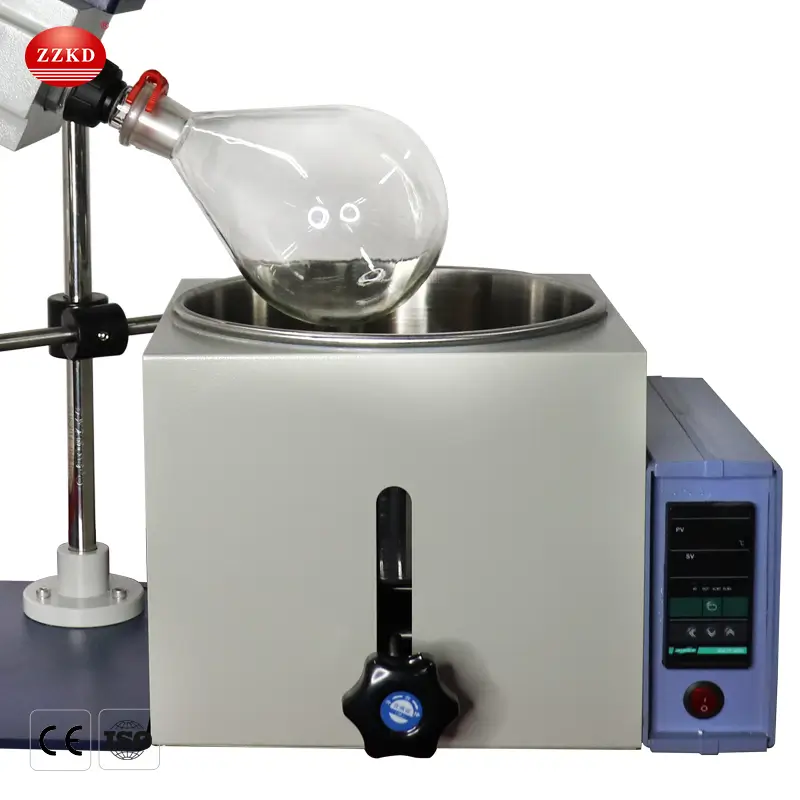
The sample (a mixture of solvent and solute) is placed in a round-bottom flask attached to the rotovap. The flask rotates slowly, creating a thin film of liquid on the inner wall.
Why rotation matters:
Increases the surface area of the sample.
Speeds up evaporation by exposing more liquid to heat and vacuum.
2. Vacuum: Lowering the Boiling Point
A vacuum pump reduces the pressure inside the system. With lower pressure, the solvent’s boiling point drops dramatically. For example, ethanol normally boils at 78°C, but under vacuum, it might boil at 30°C.
Key benefit:
Gentle removal of solvents at low temperatures, ideal for heat-sensitive materials like enzymes, fragrances, or pharmaceuticals.
3. Heating: Controlled Warmth
The rotating flask is partially submerged in a heated water or oil bath. This provides gentle, consistent heat to encourage evaporation.
Important note: The bath temperature is always set below the solvent’s normal boiling point to prevent overheating.
4. Condensation: Trapping the Solvent Vapor
The evaporated solvent travels into a condenser, where it’s cooled back into liquid form. The condenser uses cold water or a cryogenic fluid to rapidly chill the vapor.
Result:
The solvent is collected in a separate flask for reuse or disposal.
The desired compound (solute) remains in the original flask.
Key Components of a Rotary Evaporator
To visualize the process, let’s look at the main parts of a rotovap:
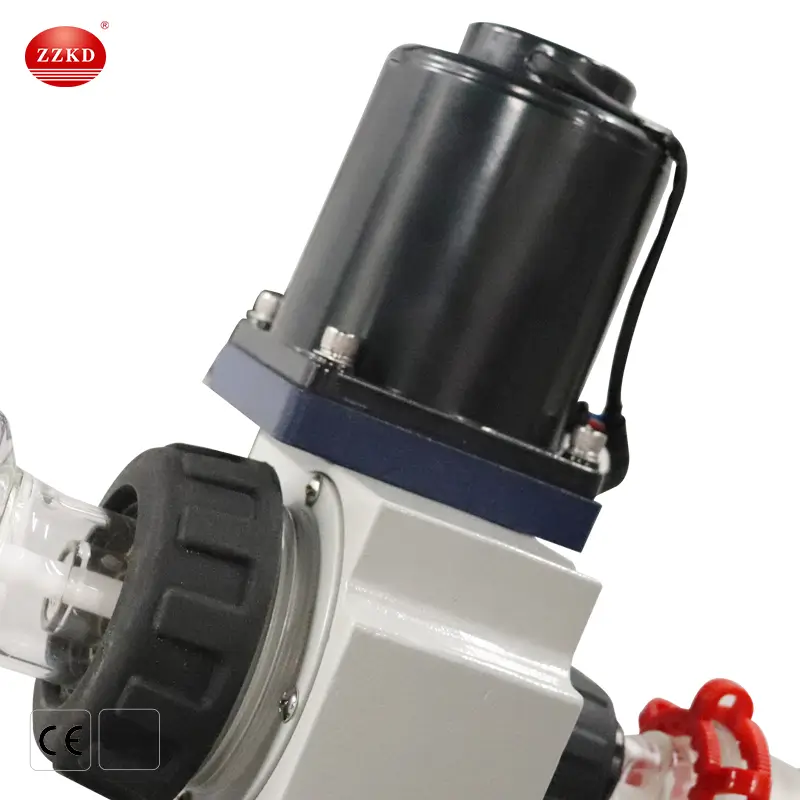
Rotating Motor: Spins the flask at adjustable speeds.
Evaporation Flask: Holds the sample and rotates to create a thin film.
Heating Bath: Provides controlled warmth (water or oil).
Condenser: Cools solvent vapor back into liquid.
Collection Flask: Stores the recovered solvent.
Vacuum System: Lowers pressure to reduce boiling points.
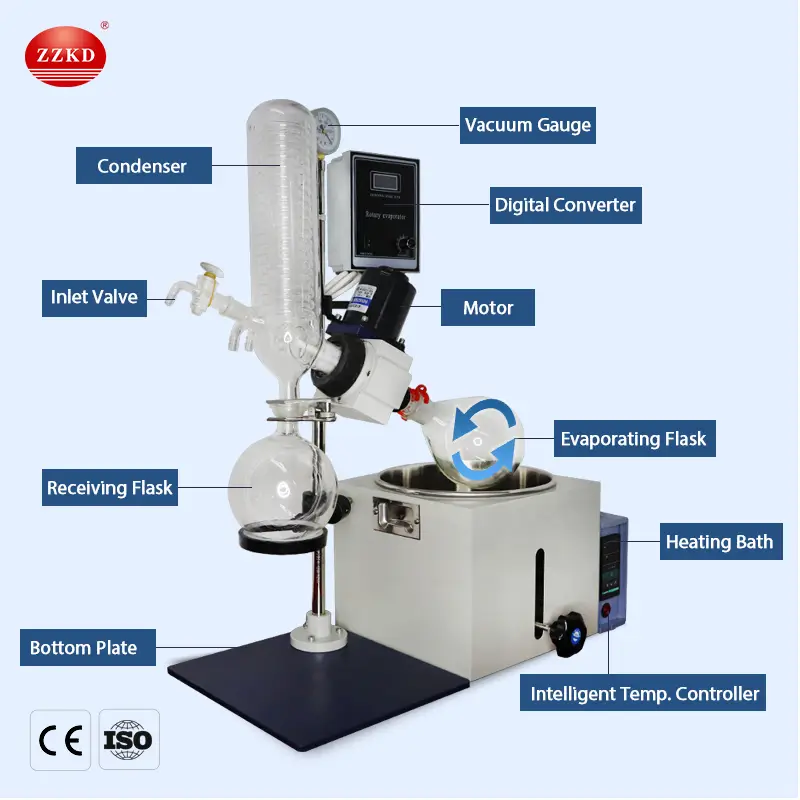

Each component works in harmony to ensure fast, efficient, and safe solvent removal.
Why Choose a Rotary Evaporator? Advantages Over Other Methods
While there are other ways to remove solvents (e.g., air drying, simple distillation), rotary evaporators stand out for several reasons:
1. Speed and Efficiency
The combination of rotation, vacuum, and heat accelerates evaporation. What might take hours with air drying can be done in minutes with a rotovap.
2. Gentle on Sensitive Samples
Low-temperature operation preserves proteins, natural extracts, and other fragile compounds.
3. Solvent Recovery
Unlike open-air evaporation, rotovaps capture up to 90% of solvents for reuse, saving costs and reducing waste.
4. Scalability
From small 50 mL flasks to industrial 50 L systems, rotary evaporators adapt to any workload.
5. User Safety
Closed systems minimize exposure to toxic solvents, protecting lab personnel.
Common Applications of Rotary Evaporators
Rotovaps are versatile tools used across industries. Here are a few examples:
Pharmaceuticals: Isolating active ingredients from plant extracts.
Chemistry Labs: Purifying synthetic compounds.
Food & Beverage: Concentrating flavors or removing alcohol from wines.
Environmental Testing: Extracting pollutants from water or soil samples.
Choosing the Right Rotary Evaporator: A Buyer’s Guide
If you’re considering purchasing a rotovap, here’s what to look for:
Capacity: Match flask size to your typical sample volume.
Vacuum Performance: A strong pump ensures efficient boiling point reduction.
Temperature Control: Precision heating protects sensitive materials.
Condenser Efficiency: Look for high cooling capacity for rapid condensation.
Build Quality: Corrosion-resistant materials (e.g., glass, PTFE) ensure longevity.
Safety Features: Automatic lift functions, overheat protection, and leak detection.
Brand Support: Choose a manufacturer with global service and spare parts.

Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To keep your rotary evaporator running smoothly:
Regularly clean glassware to prevent residue buildup.
Check vacuum pump oil levels and replace as needed.
Inspect seals and O-rings for wear.
Calibrate temperature and pressure sensors annually.
FAQs About Rotary Evaporators
Q: Can a rotary evaporator handle all solvents?
A: Most common solvents (water, ethanol, acetone) work well. For corrosive solvents, ensure compatibility with materials like PTFE or borosilicate glass.
Q: How does it compare to a standard distillation setup?
A: Rotary evaporators are faster, safer, and better for heat-sensitive materials due to lower operating temperatures.
Q: What’s the maximum temperature needed?
A: Rarely above 60°C—thanks to the vacuum, most solvents evaporate at 30–50°C.
Q: Can I recover solvents with high boiling points?
A: Yes, but a stronger vacuum or higher bath temperature may be required.
Q: Is training required to use a rotovap?
A: Basic training ensures safe operation, but modern units have intuitive controls.
Conclusion: Why Invest in a Rotary Evaporator?
A rotary evaporator is more than just lab equipment—it’s a productivity powerhouse. By combining rotation, vacuum, and controlled heating, it removes solvents faster, safer, and more efficiently than traditional methods. Whether you’re developing life-saving drugs, crafting premium cosmetics, or analyzing environmental samples, a high-quality rotovap is an indispensable tool.
As a trusted manufacturer, we design our rotary evaporators for reliability, precision, and ease of use. With customizable configurations and global service support, we’re here to meet your lab’s unique needs.
Ready to upgrade your solvent removal process? Contact us today to explore our range of rotary evaporators and discover how we can streamline your workflow!

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More