How Does a Rotary Evaporator Work? A Complete Guide
Rotary evaporators are essential tools in chemical laboratories for efficient solvent removal. This comprehensive guide explains the science behind rotary evaporation, its applications, and the benefits of various models.
vs traditional methods
Compound preservation

Science Simplified
Key Operating Principles
A rotary evaporator operates on three fundamental physical principles:
Reduced Pressure
Lowering system pressure decreases solvent boiling point, preventing thermal degradation.
Rotation
Spinning the flask increases surface area and creates a thin film for rapid evaporation.
Condensation
Cooled condenser captures vaporized solvent for recovery or disposal.
Why is reducing pressure important in a rotary evaporator?
Lowering pressure significantly reduces the solvent's boiling point. This allows evaporation at temperatures far below normal boiling points, preserving heat-sensitive compounds that would degrade at higher temperatures. For example, water evaporates at just 30°C under vacuum as opposed to 100°C at sea level pressure.
Core Technology
Main Components Explained
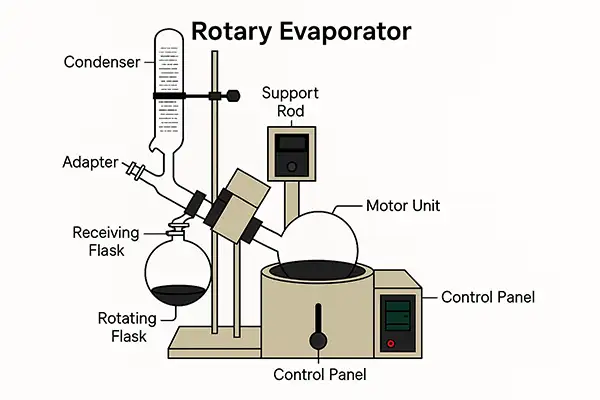
Rotating Flask
Holds sample & creates thin film
Heating Bath
Gentle thermal energy source
Condenser
Cools vapor back to liquid
Receiving Flask
Collects condensed solvent
Vacuum Pump
Reduces system pressure
Control System
Precise operation management
Procedure
Step-by-Step Evaporation Process
Sample Placement
The solution containing the solvent is placed in the evaporation flask, filling no more than half of its capacity to prevent overflow during rotation.
Immersion & Rotation
The flask is partially submerged in the temperature-controlled water or oil bath and set to rotate slowly at 50-200 rpm, creating a uniform solvent film.
Vacuum Application
The vacuum pump reduces system pressure to 10-100 mbar (depending on solvent) to lower the boiling point of the solvent.
Gentle Heating
The bath heats the rotating solvent to a temperature below its atmospheric boiling point, causing evaporation.
Vapor Condensation
Solvent vapor travels upward through the vapor tube to the condenser where it's cooled and liquified.
Solvent Collection
The condensed liquid drips down the condenser coils into the collection flask where it's recovered or disposed of.
What is the main advantage over simple distillation?
Rotary evaporation is significantly more efficient and preserves sensitive compounds through lower operating temperatures. This process achieves higher evaporation rates due to the large solvent surface area created by rotation. Additionally, the integrated vacuum system allows for continuous solvent removal without interruption, making it perfect for heat-sensitive compounds in analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical purification, and food science applications.
Can rotary evaporators be used for large-scale production?
Absolutely. While standard rotary evaporators are designed for laboratory use, industrial-scale systems can process substantial volumes. For example, the RE-5002 Large Scale System features a 10-liter evaporation capacity, automated controls, and advanced safety systems, making it suitable for pilot plants and production facilities.
Industry Applications
Pharmaceuticals
Purification of drug compounds and removal of reaction solvents while preserving molecular integrity.
Recommended Models
Top-rated rotary evaporators by capacity and features:
RE-201D 2L System
Ideal for small laboratoriesRE-501 5L Professional
Enhanced capacity and efficiencyR-1020 20L Industrial
Industrial-scale productionE-2000ABE Mini
Compact benchtop solution

Technical Information
Maintenance & Safety Guidance
Routine Maintenance
Daily: Clean evaporating and collecting flasks using appropriate solvents
Weekly: Perform safety checks on vacuum seals and rotating joints
Monthly: Replace vacuum pump oil and check refrigeration levels
Quarterly: Inspect electrical components and temperature sensors
Annual: Professional calibration and comprehensive system inspection
Critical Safety Practices
Never overfill the evaporation flask (max 50% capacity)
Implement secondary protection against implosion with safety glasses
Only use bath fluids appropriate for the temperature range
Always release vacuum pressure before disconnecting components
Place emergency release valves and fire suppression equipment nearby
Scientific Outlook
The Future of Evaporation Technology
Laboratory evaporation technology continues to evolve rapidly. According to recent studies at MIT and ETH Zurich, emerging trends include:
Automated Systems
Self-regulating, AI-driven evaporation that automatically adjusts parameters to maximize efficiency and prevent bumping.
Energy Recovery
New designs capture thermal energy from condensation to preheat incoming materials, reducing energy consumption by 30%.
Parallel Processing
Multi-rotovap systems with synchronized controls allow simultaneous evaporation of multiple solvent systems within a fume hood.

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More