Laboratory Rotary Evaporator Guide
Master safe and efficient operation of rotary evaporators with our comprehensive manual
How to Use Rotary Evaporator: Step-by-Step Guide
A rotary evaporator, often abbreviated to "rotovap," is an essential piece of equipment in chemical laboratories for the gentle and efficient removal of solvents from samples. Its design allows for reduced pressure evaporation, enabling lower boiling temperatures and protecting sensitive compounds.

Lab technicians using modern rotary evaporator system
Core Components & Assembly
The rotary evaporator consists of several primary components: a motor unit to rotate the evaporation flask, a vacuum system to lower the pressure, a heated water or oil bath, a condenser with cooling water circulation, and a receiving flask for collected solvent.
In practical terms, it is used in applications such as botanical extraction, pharmaceutical formulation, polymer research, and academia. For example, a 2L rotary evaporator is often the choice for research institutes needing small to medium sample processing.
Why Use Reduced Pressure Evaporation?
Lowering the pressure enables solvent evaporation at temperatures far below their normal boiling point, which preserves heat-sensitive molecules. According to an MIT research report, reduced pressure evaporation can decrease degradation rates of thermolabile compounds by up to 70%, making rotovaps critical for modern chemistry labs.
Step-by-Step Operational Guide
Setup and Inspection: Check that all glassware is clean and free of cracks. Ensure that seals are in good condition and vacuum tubing is secure.
Fill the Heating Bath: Use distilled water (or oil for higher temperature requirements). Set the bath to the desired temperature (typically 40-60°C).
Attach the Sample Flask: Securely clamp the round-bottom flask to the rotary motor.
Apply Vacuum: Gradually reduce the pressure to the desired level (0.1-0.3 bar) to prevent bumping.
Begin Rotation: Rotate the flask at 100-200 RPM for optimal results.
Monitor Condensation: Solvent vapors pass into the condenser and liquefy into the receiving flask.
Completion and Shutdown: Once evaporation is complete, stop rotation, release vacuum slowly to atmospheric pressure, and remove the flask.
Advanced Techniques & Best Practices
Efficiency Enhancement Methods
To maximize rotary evaporator performance, consider these advanced approaches:
| Method | How it Works | Effectiveness Rating |
|---|---|---|
| Gradient Vacuum | Gradually reduce pressure as evaporation progresses | ★★★★☆ |
| Antibumping Granules | Use inert solids to prevent violent boiling | ★★★☆☆ |
| Co-Solvent Technique | Add lower boiling point solvent for enhanced evaporation | ★★★★★ |
| Optimized Condenser Cooling | Use chiller or glycol for efficient condensation | ★★★★☆ |
Safety Protocols in Operation
Essential Safety Checklist
Always inspect glassware for cracks before use
Wear protective lab gear: goggles, gloves, and lab coat
Do not overfill the evaporation flask (max 50% capacity)
Gradually apply and release vacuum
Avoid These Risks
Never use with incompatible solvents
Avoid water bath overflow
Prevent bumping with proper technique
Maintain ventilation during operation
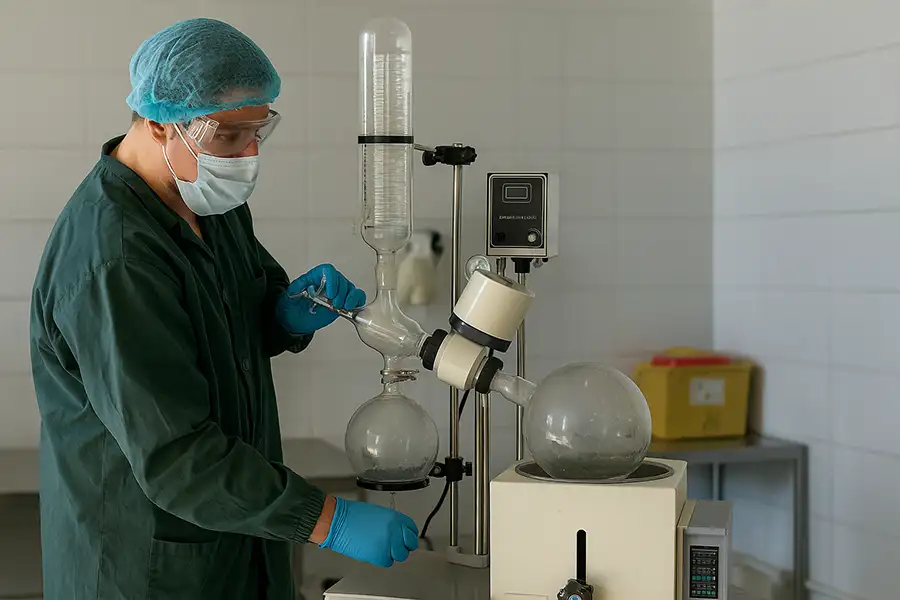

Lab tech demonstrating safe operation protocols
Rotavap Models & Selection
Choosing the right rotary evaporator depends on volume, solvent type, and usage frequency:

Small Rotary Evaporator
Ideal for research & education
100-1000 ml capacity
Compact footprint
Perfect for teaching labs

2L & 5L Systems
Standard research systems
Medium sample processing
Daily processing of up to 20 samples
Pharmaceutical applications

Industrial Rotavaps
20-100 liter capacity
Continuous production
Automated operation
High-throughput processing
Performance Trends
Modern units provide significant efficiency gains over older models

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More