Understanding Rotary Evaporator Chemistry
Rotary evaporator chemistry plays a crucial role in laboratories and chemical industries, providing a safe and efficient method for solvent evaporation. A rotary evaporator—often called a "rotovap"—is commonly used in organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals, food science, and many other fields.
In simple terms, it allows the removal of solvents from samples by evaporation under reduced pressure, significantly speeding up the process and reducing thermal degradation.
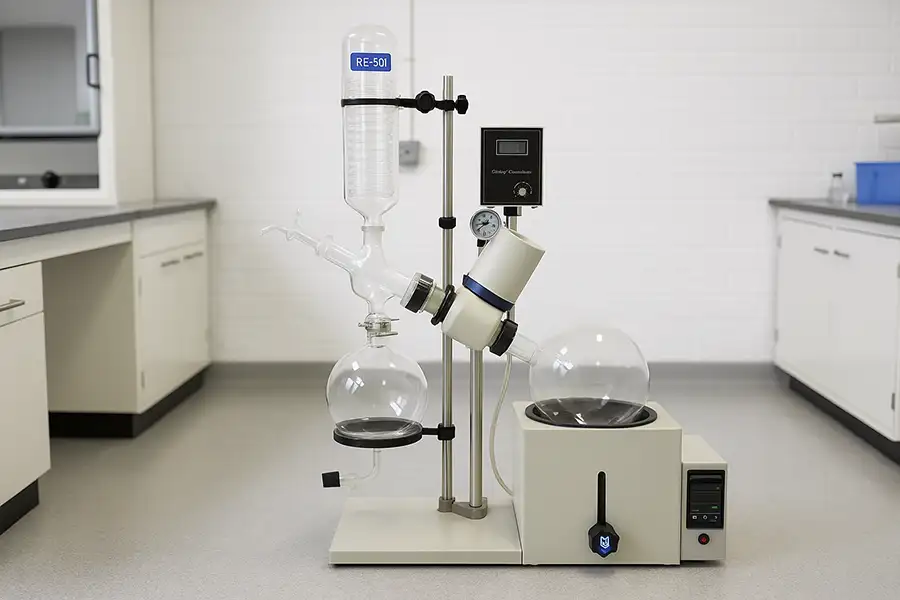

Modern rotary evaporator setup with vacuum pump and cooling system
What is a Rotary Evaporator?
The principle of operation for a rotary evaporator is straightforward but effective. It involves a rotating flask partially immersed in a water or oil bath, connected to a vacuum pump, and paired with a cooling condenser. This setup reduces the boiling point of the solvent, allowing it to evaporate at much lower temperatures. The vapors then condense back into liquid in a separate flask for collection.
Modern rotary evaporators come in a variety of sizes, from small mini rotary evaporators suitable for teaching labs to large-scale models for industrial applications. For example, a 2L rotary evaporator might be perfect for small-scale organic synthesis work, while a large scale rotary evaporator can handle batch solvent recovery for manufacturing facilities.
Core Components of a Rotary Evaporator
Rotary Motor
Ensures rotation of the flask, increasing surface area for evaporation. Higher speed provides more efficient evaporation.
Heating Bath
Usually filled with water or oil, controls temperature precisely using digital thermostats for optimal evaporation.
Vacuum Pump
Lowers internal pressure to reduce boiling points, with multiple vacuum levels available for different solvents.
Condenser
Utilizes cooling fluids to convert vapors back into liquid form, with efficient cooling systems for maximum recovery.
Receiving Flask
Collects the distilled solvent, available in various sizes and materials to meet specific application requirements.

Technical diagram showing components of a modern rotary evaporator
Applications in Chemistry
Rotary evaporator chemistry has a wide spectrum of applications across various scientific disciplines:
1 Organic Synthesis
Removing reaction solvents to purify products without thermal degradation.
2 Pharmaceuticals
Concentrating extracts and filtrates while preserving active ingredients at low temperatures.
3 Food Science
Concentrating flavors and removing unwanted volatiles for enhanced taste profiles.
4 Environmental Analysis
Concentrating pollutants from water samples for more accurate detection.
5 Biochemical Research
Gentle concentration of biological samples without denaturing proteins.
6 Essential Oil Extraction
Efficient removal of solvents from delicate aromatic compounds.

Chemist preparing pharmaceutical samples using a rotary evaporator
Scientific Perspective and Data
Rotary evaporators have dramatically improved laboratory workflow efficiency. According to research from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), improvements in lab automation, including rotary evaporation systems, can reduce solvent recovery time by over 60% in controlled environments.
Operational Efficiency
The same study noted that modern rotary evaporators can process 45% more samples per day compared to traditional evaporation methods.
Environmental Impact
These efficiency gains not only save operational costs but also reduce environmental impact by lowering energy consumption by 25-40%.
Popular Equipment Models
Here are our most requested rotary evaporator models suitable for various laboratory needs:
| Model | Capacity | Special Features | Applications | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE-201D Rotary Evaporator | 2L | Digital temp control Automatic lift | Small-batch organic synthesis | Details |
| RE-501 Rotary Evaporator | 5L | Multistage vacuum Safety sensors | Medium-scale lab processing | Details |
| R-1020 Rotary Evaporator | 20L | Industrial cooling Automation ready | Large laboratory or pilot plant | Details |
| RE-2000ABE Precision Series | 1L | Microprocess control Glass visualization | Pharmaceutical research | Details |
Conclusion
Rotary evaporator chemistry is essential for modern science and industry. By leveraging reduced pressure and efficient heat transfer, rotary evaporators provide a safe, energy-efficient, and scalable means for solvent evaporation and recovery. From small lab setups to industrial-scale systems, this technology continues to evolve, offering solutions for faster, safer, and more sustainable chemical processing.
The continuous innovation in rotovap technology includes enhanced automation, integrated vacuum systems, and environmentally friendly designs that significantly reduce solvent waste while improving user safety.

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More