Understanding Rotary Evaporators
Efficient Solvent Removal for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
What Does a Rotary Evaporator Do?
Essential Tool for Gentle Solvent Removal in Scientific Applications
In laboratories and chemical production facilities, precision and efficiency are critical. One of the most important tools used for solvent removal and concentration is the rotary evaporator. But what does a rotary evaporator do? This article will break down its function, applications, and why it’s indispensable in modern science.

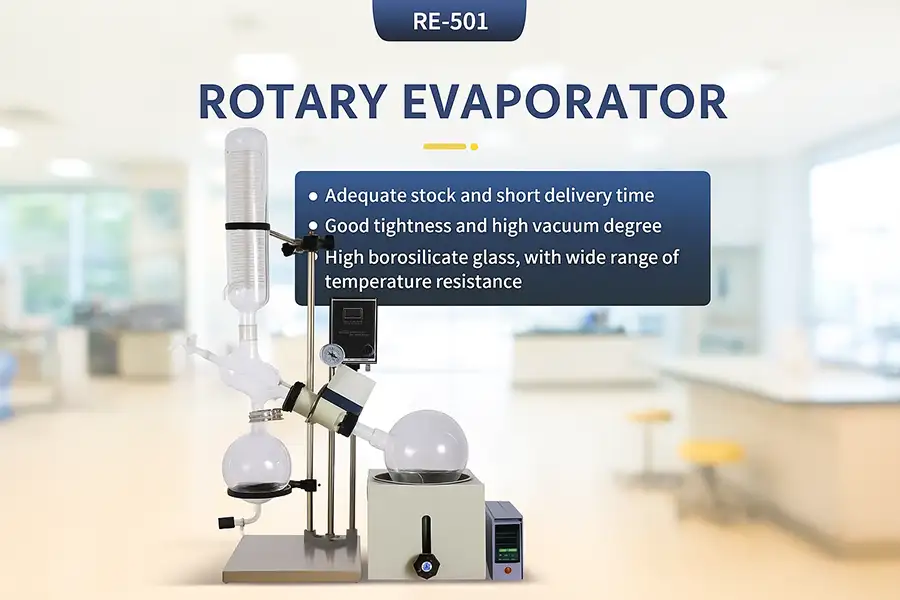
Visual Representation of Rotary Evaporator
Modern rotary evaporator in laboratory setting showing evaporation process
Understanding the Basics
A rotary evaporator, often called a "rotovap", is a device used to remove solvents from samples by evaporation under reduced pressure. It works by rotating a flask containing the sample in a heated water or oil bath while applying a vacuum. This combination lowers the boiling point of the solvent, allowing it to evaporate at lower temperatures, which is especially useful for heat-sensitive compounds.
Why is reduced pressure important in rotary evaporation?
Key Components of a Rotary Evaporator
Rotating Flask
Holds the sample and increases surface area for faster evaporation
Heating Bath
Provides controlled heat to accelerate the evaporation process
Condenser
Cools vapor back to liquid form for collection
Receiving Flask
Collects the condensed solvent for reuse or disposal
Applications in Science and Industry
Industrial Applications
Essential oil extraction
Pharmaceutical purification
Solvent recovery systems
Chemical synthesis
Laboratory Applications
Concentrating solutions
Removing solvents after extraction
Purifying chemical compounds
Sample preparation for analysis
For example, a 2L rotary evaporator is ideal for small-scale laboratory work, while a 5L rotary evaporator suits medium-scale operations. Larger models like the 10L rotary evaporator are perfect for industrial-scale solvent removal.
Can rotary evaporators be used for large-scale production?
Scientific Insight & Research
According to a study by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), technological advancements in laboratory equipment have increased efficiency by up to 40% over the past decade. This includes innovations in rotary evaporation technology, which now offer better temperature control, improved vacuum systems, and enhanced safety features.

Modern rotary evaporator technical documentation showing setup and safety procedures
Specification Comparison
| Model | Capacity | Rotation Speed | Heating Power | Best Use | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE-201D | 2L | 20-180 rpm | 1 kW | Small-scale laboratory work | $500-$1,000 |
| RE-501 | 5L | 10-200 rpm | 2 kW | Medium-scale operations | $800-$1,200 |
| RE-1002 | 10L | 5-150 rpm | 3.5 kW | Industrial-scale evaporation | $1,000-$1,500 |
Comparison of popular rotary evaporator models with detailed specifications
Conclusion
So, what does a rotary evaporator do? It enables efficient, gentle removal of solvents from samples, protecting sensitive compounds and improving productivity. From small laboratory setups to large-scale industrial production, rotary evaporators are versatile, reliable, and essential tools in modern science.
Is investing in a rotary evaporator worth it?
Ready to Optimize Your Lab?
Contact us today to find the perfect rotary evaporator for your needs

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
How Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read MoreComplete Guide to 50L Rotary Evaporators
Complete guide to 50 liter rotary evaporators - working principles, applications, and industrial significance...
Read More