What Exactly is a Rotovap and How Does It Work?
Are you finding it hard to separate solvents from your samples? Old ways can be slow and might harm your delicate compounds. There is a better method.
A rotovap, short for rotary evaporator, is a special lab tool. We use it to gently and quickly remove solvents from samples by making them evaporate under low pressure.

I've been in the business of making and exporting lab equipment for over 16 years. In my experience, knowing your tools well is very important. Let's look at what a rotovap does for your lab. We can see how its smart design helps your work go smoothly. As a company, we focus on making these tools reliable and easy to use for scientists worldwide.
What are the Key Components of a Rotovap and How Do They Work Together?
Do the different parts of a rotary evaporator confuse you? It might look complicated. But, understanding each part helps you use it best.
A rotovap has a few main parts. These include a heating bath, a spinning flask, a condenser, a vacuum system, and a flask to collect the solvent. They all work together to evaporate and then turn solvents back into liquid.
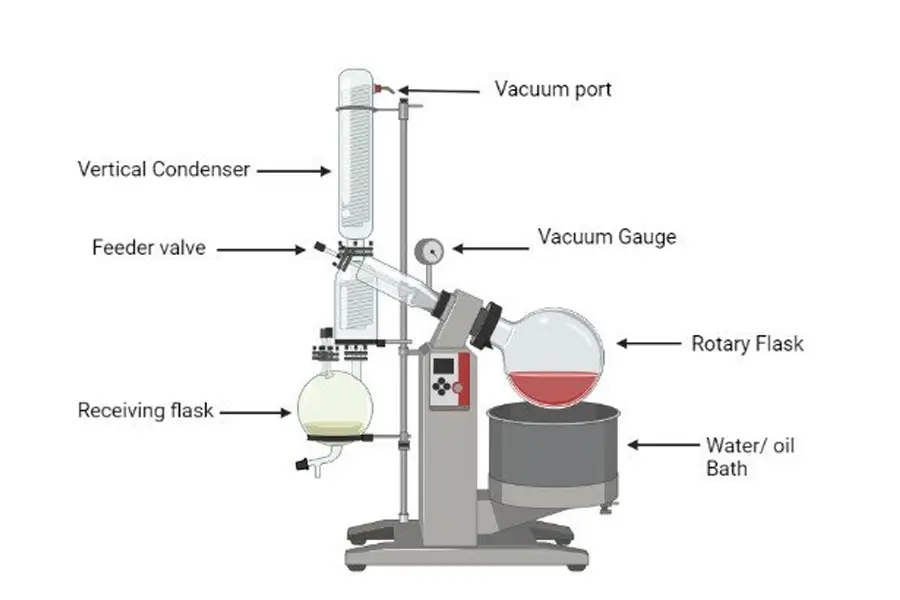
Let me explain how these parts cooperate. It’s quite an elegant system. I've spent many hours with our engineers discussing how to optimize each component for better performance and durability. We are proud of the precision we achieve.
1. Heating Bath
This part gently warms your sample. Controlled heating is super important. It prevents your sample from getting too hot too fast. We make water baths for temperatures up to 99°C. For higher temperatures, we offer oil baths. I remember a client from a university research lab. They had trouble with samples breaking down. We helped them adjust their bath temperature settings. It made a big difference in their results.
2. Rotating Flask (Evaporating Flask)
Your sample goes into this flask. The flask spins. This spinning spreads the sample into a thin film. This larger surface area helps the solvent evaporate faster. It also stops the sample from bumping or boiling over. We produce these flasks in many sizes. For small experiments, a 2L rotary evaporator flask might be enough. For bigger jobs, we have flasks like our popular 5L rotary evaporator, or even up to a 50L rotary evaporator for larger amounts.
3. Vacuum System
This system lowers the air pressure inside the rotovap. When the pressure is lower, solvents boil at lower temperatures. This is very important for gentle evaporation. It protects heat-sensitive materials. We always advise our customers on choosing the right vacuum pump.
4. Condenser
The condenser cools down the solvent vapor. This turns the vapor back into a liquid. The liquid solvent then drips into the collection flask. There are different condenser designs, like diagonal or vertical. The choice depends on your solvent and lab space. We've helped many customers pick the best one for their specific needs.
5. Receiving Flask (Collection Flask)
This is where the condensed, liquid solvent is collected. It’s usually easy to remove so you can recover your solvent. Our design ensures a good seal here too.
All these parts must work perfectly together. That's what we focus on in our manufacturing – ensuring each part of the rotary evaporator machine is top quality.
What are Rotovaps Used For in Different Industries?
Are you wondering if a rotovap is suitable for your work? You might be surprised by how many uses it has. Don't overlook this strong tool.
Rotovaps are used a lot in chemistry to remove solvents. Pharma companies use them to concentrate samples. Food scientists use them to get flavors. Even cannabis processors use them for purification.

It's amazing to see the range of applications for rotovaps. Over my 16 years exporting these machines, I've seen them go into so many different types of labs. We always try to understand our customer's specific industry needs.
Chemical & Pharmaceutical Companies
This is a very big field for us. These companies use rotovaps every day. They use them for making new chemicals, purifying compounds, and concentrating active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Our laboratory rotary evaporator models are ideal for their research and development labs. I once worked with a pharmaceutical client who needed a special setup for a very tricky solvent. We designed a custom solution for them. It greatly improved their product yield and safety. It was a proud moment for our team.
Academic Universities & Research Institutions
Almost every chemistry lab in a university has at least one rotovap. They are essential for both research projects and for teaching students. We have supplied our equipment to countless universities all over the world. We often get feedback on how our rotovaps help their students learn practical lab skills.
Food & Beverage Industry
In this industry, rotovaps help extract flavors and smells. They can concentrate fruit juices or remove alcohol from beverages. For example, they are used to make high-quality essential oils or to create concentrated food flavorings. The gentle evaporation helps keep the delicate flavors intact.
Cannabis & Hemp Processing Facilities
This is a quickly growing area. Here, rotovaps are key for removing solvents like ethanol after extraction. They are also used to purify cannabinoids like CBD and THC. Our large scale rotary evaporator units are very popular in this sector due to their efficiency for bigger batches. We ensure our equipment meets their specific regulatory needs.
Environmental Testing Laboratories
These labs use rotovaps to prepare samples for analysis. For instance, they might need to concentrate pollutants from water or soil samples to detectable levels. Accuracy is critical here, and our equipment helps them achieve that.
| Industry | Common Rotovap Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemistry | Solvent removal, sample concentration, purification |
| Pharmaceuticals | API concentration, drug development, quality control |
| Academia | Research experiments, teaching laboratory techniques |
| Food & Beverage | Flavor extraction, juice concentration, dealcoholization |
| Cannabis/Hemp | Solvent recovery, cannabinoid purification |
| Environmental | Sample preparation, pollutant concentration |
This table gives a quick overview, but there are many more specific uses within each field. We always try to learn about new applications from our customers.
How Do I Choose the Right Rotovap for My Needs?
Feeling lost with all the rotovap choices available? Picking the wrong one can cost you time and resources. Let's make this decision simpler for you.
Think about your sample size, the type of solvent you use, the vacuum level you need, the temperature range, and your budget. Also, consider features like automatic lift or digital controls.

Choosing the right rotovap is crucial for smooth lab operations. As a manufacturer, I always tell my customers to think carefully about their current and future needs. It's better to choose a slightly more versatile model if you expect your work to change.
Key Factors to Consider:
Sample Volume / Flask Size: This is usually the first thing to decide. How much material do you typically process? We offer a wide range. You can get a small rotary evaporator, sometimes called a mini rotary evaporator, with 1L or 2L flasks for smaller tasks. We also have 5L, 10L, 20L, and even up to 50L models for pilot-scale work or small production runs. I often ask clients, "What's your usual batch size?" This helps narrow down the options.
Solvent Type: What solvents will you be using? Some aggressive solvents can damage certain types of seals or glassware. We offer different seal materials like PTFE for good chemical resistance. It's important to match the rotovap materials to your chemicals.
Temperature Range: Standard water baths heat up to about 99°C. If you need higher temperatures for solvents with high boiling points, an oil bath is necessary. Oil baths can go up to 180°C or more with our models.
Vacuum Source and Control: Do you already have a lab vacuum source, or do you need a dedicated pump? How much control do you need over the vacuum level? Precise vacuum control can be very important for difficult separations or very sensitive compounds.
Condenser Type: There are diagonal condensers for general use. Vertical condensers are good if you have solvents with low boiling points or limited space in your fume hood. Cold finger condensers are for very volatile solvents. We can help you pick the right one.
Automation and Safety Features: Features like a motorized lift for the flask make operation easier and safer. Digital displays for temperature and rotation speed provide better control. Over-temperature protection is an important safety feature. We have manual lift models which are more budget-friendly, and automated models for more convenience.
Budget: Of course, price is a factor. We believe in offering "Made in China + International Quality." This means you get a high-value, reliable machine that meets international standards like CE and ISO9001, but at a good price.
I always advise new buyers to list their top three requirements. Then we can find the best match. It’s like buying a car: you need to know if you mostly drive in the city or if you need something for long trips before you pick a model. We are here to guide you through these choices.
What Safety Precautions Should I Take When Using a Rotovap?
Are you concerned about safety while using a rotary evaporator? Accidents can occur with any lab equipment if it's not handled correctly. It's important to protect yourself and your lab.
Always put on proper personal protective equipment (PPE). Check that glassware has no cracks. Use a safety shield if possible. And never leave a running rotovap alone for too long.

Safety is the most important thing in any lab. At our company, we build safety features into our equipment, but users also need to follow good lab practices. I've visited many labs, and good safety habits always stand out.
Essential Safety Practices:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): This is non-negotiable. Always wear safety glasses or a face shield. This protects your eyes from splashes or in the rare case of glassware breaking under vacuum (implosion). A lab coat and appropriate gloves are also essential.
Glassware Inspection: Before you start, carefully check every piece of glassware. Look for cracks, chips, or star-like fractures. Even a small flaw can weaken the glass, and it might fail under vacuum or when heated. I cannot stress this enough. We learned about an incident at a university. A tiny, unnoticed crack in a flask led to it breaking. Luckily, no one was injured, but it was a serious reminder.
Secure Connections: Make sure all glass joints are correctly greased (if your system requires it) and secured. Use Keck clips or similar fasteners. This helps maintain the vacuum and prevents parts from coming loose.
Heating Bath Safety: Fill the heating bath to the correct level. Do not overfill. Be careful not to overheat the bath, especially if you are using flammable solvents. And remember, the bath surface can be very hot.
Rotation Speed: Start the flask rotation slowly. Make sure the flask is balanced. If the load is unbalanced and the speed is too high, it can cause problems or even damage the equipment.
Vacuum Application and Release: Apply the vacuum slowly and release it slowly. If you do it too quickly, your solvent might boil too vigorously (this is called bumping) or get sucked into the vacuum pump. A bump trap between the evaporating flask and the condenser can help prevent this.
Solvent Compatibility: Know the properties of the solvents you are working with. Are they flammable? Are they reactive? Always work in a well-ventilated area or, ideally, inside a fume hood.
Never Run Dry: Do not let the evaporating flask boil completely dry. Some residues can become unstable or even explosive when dry and hot.
Cooling System Check: Ensure that your coolant (usually water) is flowing through the condenser before you start heating the sample. No cooling means no condensation.
Avoid Overfilling Flask: Do not fill the evaporating flask more than halfway. For some foamy materials, even one-third full is better. This gives space for boiling and prevents bumping.
Following these simple rules will make your work with a rotovap much safer. We also provide detailed operating manuals with all our equipment that include safety guidelines.
Conclusion
Rotovaps are essential tools for removing solvents efficiently. Understanding their parts, uses, how to choose one, and safety rules will greatly improve your lab work. We are committed to helping you succeed with our equipment.

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More