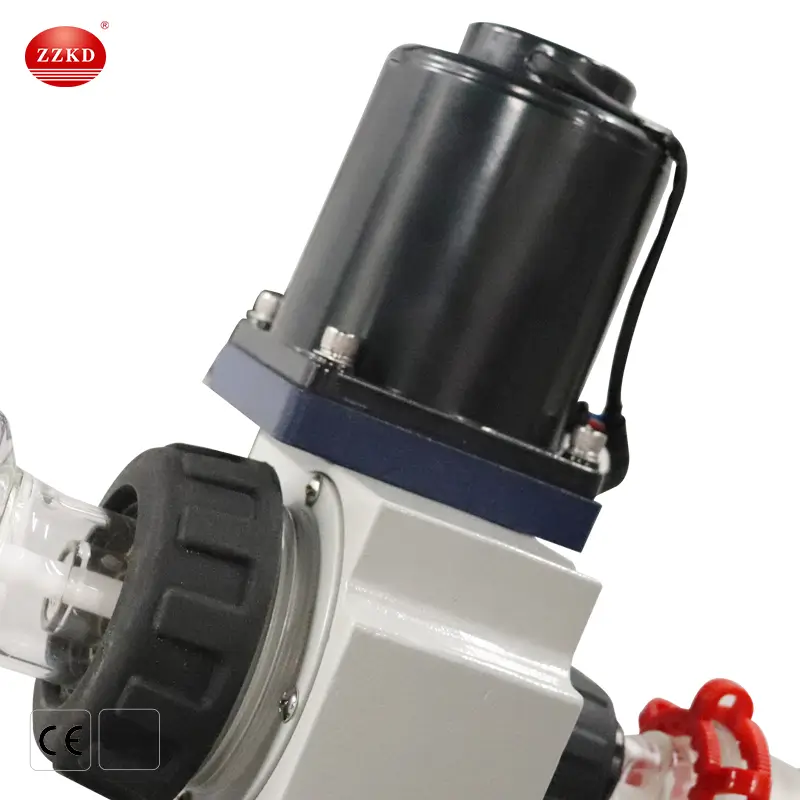
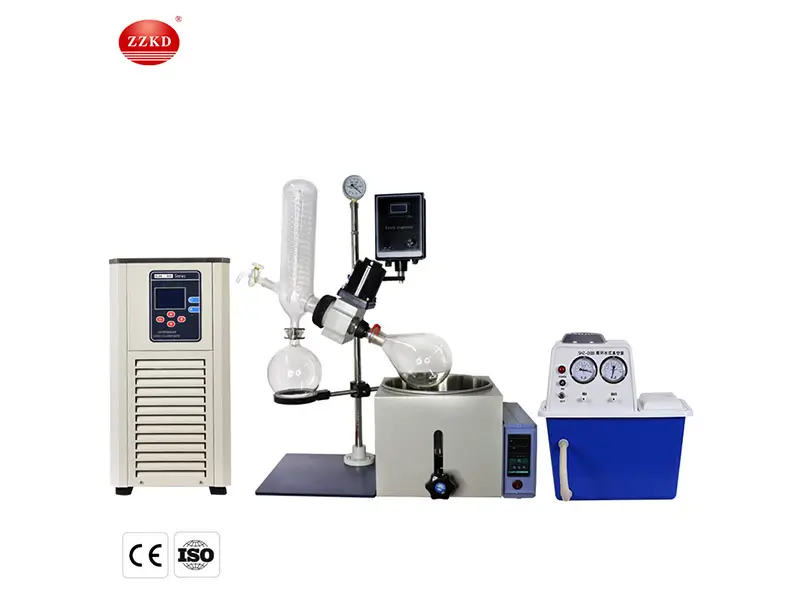
What is a Rotovap Used For?
If you’ve ever wondered how scientists, chemists, or manufacturers efficiently separate liquids from mixtures, the answer often lies in a device called a rotary evaporator, or rotovap for short. Whether you’re working in a lab, a production facility, or even a cannabis extraction plant, rotary evaporators are essential tools for many industries.

1. What is a Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap)?
Let’s start with the basics. A rotary evaporator is a laboratory instrument designed to gently and efficiently remove solvents from liquid mixtures using evaporation. Imagine you’ve mixed two liquids—say, water and alcohol—and you want to separate them without losing the valuable components. A rotovap makes this process faster, safer, and more controlled than traditional methods like simple distillation.
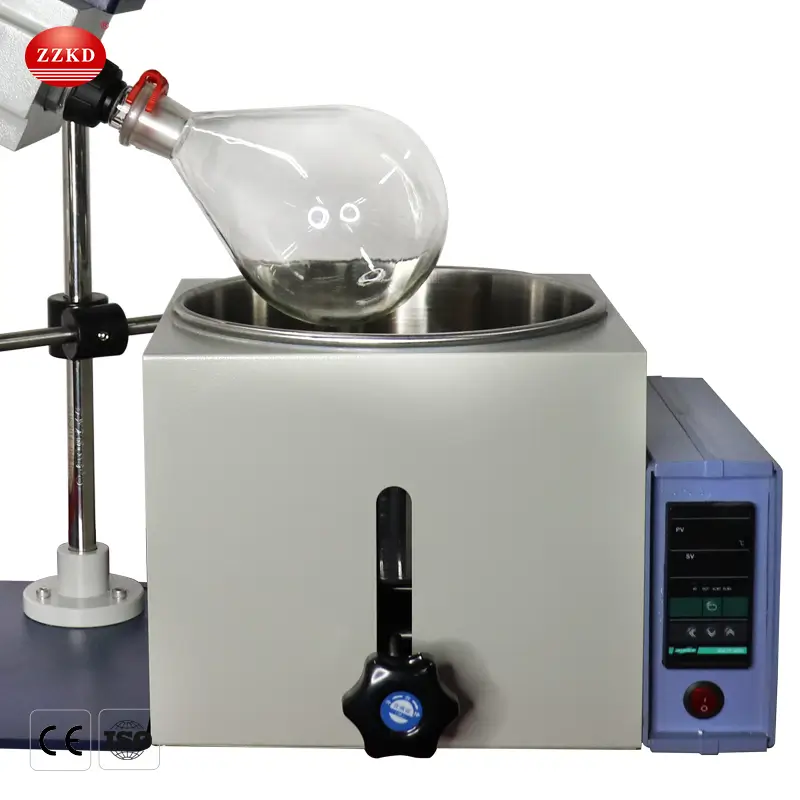
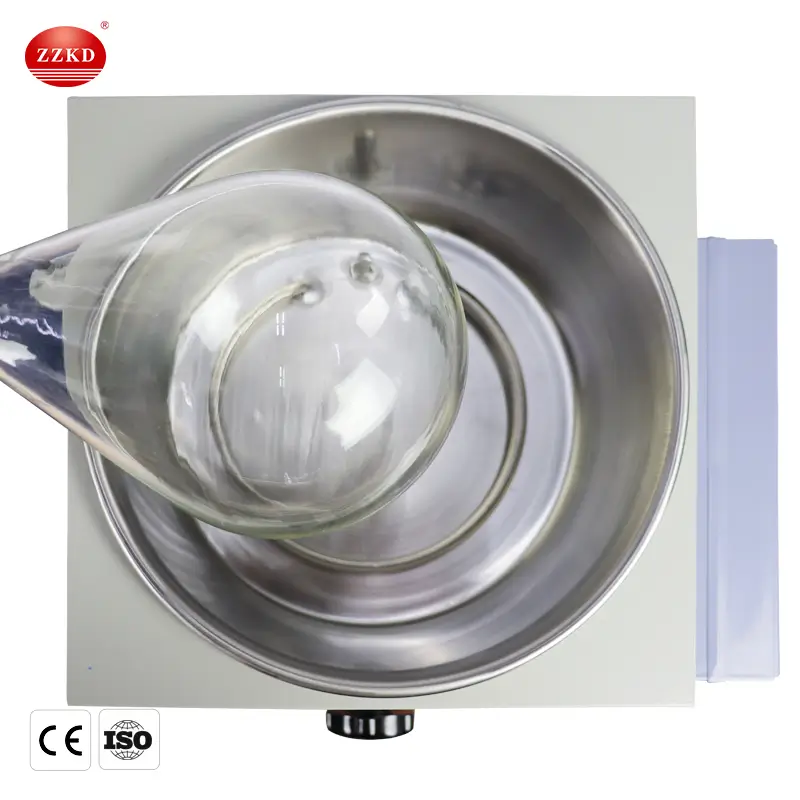
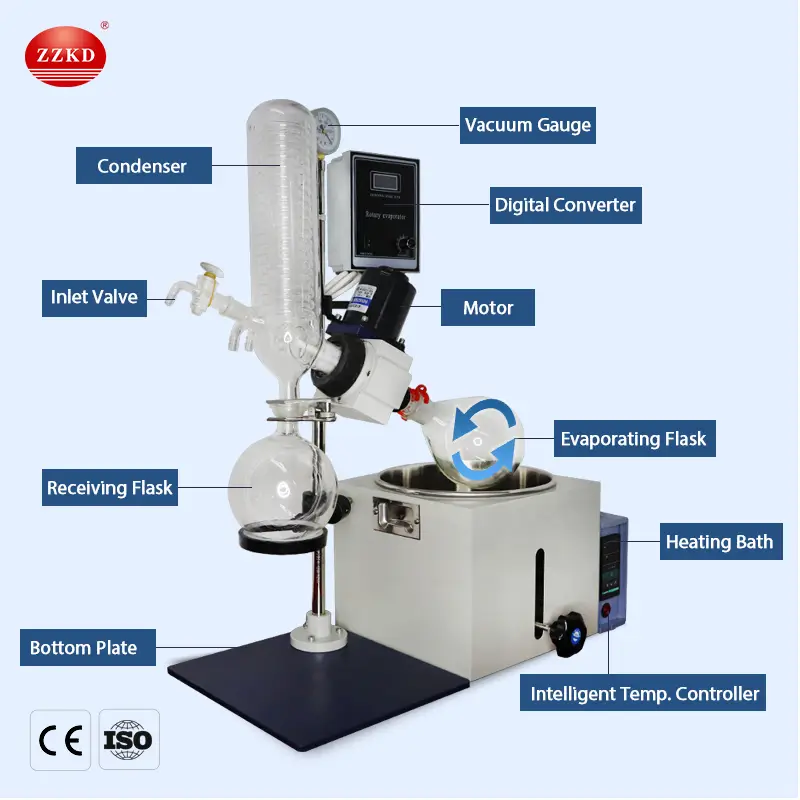
The device consists of a few main parts:
A rotating flask that holds the liquid mixture.
A heating bath to warm the solution.
A condenser to cool and collect the evaporated solvent.
A vacuum pump to lower the pressure inside the system.
By combining rotation, heat, and vacuum, the rotovap speeds up evaporation while protecting sensitive materials from high temperatures.

2. How Does a Rotovap Work?
To understand why rotovaps are so useful, let’s walk through the process step by step:
Step 1: Lowering the Pressure
The vacuum pump reduces air pressure inside the system. Lower pressure means liquids evaporate at lower temperatures. For example, water normally boils at 100°C (212°F), but under vacuum, it can boil at 40°C (104°F) or even lower. This protects heat-sensitive materials (like vitamins or plant extracts) from getting damaged.
Step 2: Gentle Heating
The rotating flask is partially submerged in a heated water or oil bath. The heat provides energy to help the solvent evaporate, while the rotation spreads the liquid into a thin film inside the flask. This thin film increases the surface area, making evaporation faster and more efficient.
Step 3: Cooling and Collecting
As the solvent evaporates, it travels into the condenser, which is cooled by circulating water or a chiller. The vapor turns back into liquid and drips into a collection flask. The desired compound (the “non-volatile” part) stays behind in the rotating flask.
Step 4: Recovery
Once the process is complete, you’re left with two separate components: the purified solvent in the collection flask and the concentrated product in the rotating flask.
3. Key Applications of Rotary Evaporators
Rotovaps are incredibly versatile. Here are some of the most common industries and tasks where they shine:
Pharmaceuticals and Research Labs
Drug Development: Isolating active ingredients from raw materials.
Purification: Removing impurities or solvents from synthesized compounds.
Sample Preparation: Concentrating samples for analysis.
Food and Beverage Industry
Extracting Flavors: Capturing natural essences from fruits, herbs, or spices.
Decaffeination: Removing caffeine from coffee or tea without harsh chemicals.
Concentrating Juices: Creating syrups or powders by gently removing water.
Essential Oils and Cannabis Extraction
Distilling Oils: Separating essential oils from plant material.
CBD/THC Isolation: Purifying cannabinoids from cannabis extracts.
Chemical Manufacturing
Solvent Recovery: Reusing expensive solvents like ethanol or acetone.
Polymer Production: Concentrating liquid polymers.
Environmental Testing
Analyzing Pollutants: Concentrating water or soil samples to detect contaminants.
4. Why Use a Rotovap Instead of Other Methods?
You might ask: “Can’t I just boil the mixture to separate the liquids?” While simple distillation works for some tasks, rotovaps offer unique advantages:
Lower Temperatures: The vacuum allows evaporation at reduced temperatures, protecting delicate compounds (e.g., vitamins, fragrances, or cannabinoids) from thermal degradation.
Faster Results: Rotation creates a thin film of liquid, speeding up evaporation.
Higher Precision: Control over temperature, pressure, and rotation speed ensures consistent results.
Safer Operation: Closed systems minimize exposure to toxic fumes.
Cost-Effective: Recovering solvents saves money and reduces waste.

5. How to Choose the Right Rotary Evaporator
If you’re considering buying a rotovap, here are the key factors to keep in mind:
Capacity
Rotovaps come in different sizes, from small benchtop units (0.5–2L flasks) for research labs to large-scale systems (10L+ flasks) for industrial production. Match the flask size to your typical sample volume.
Vacuum Performance
A strong vacuum pump is critical for efficient evaporation. Look for pumps that can achieve at least 10 mbar (0.01 atm) of pressure. Oil-free pumps are easier to maintain.
Heating Bath Temperature
Most rotovaps use water baths, but models with oil baths can reach higher temperatures (up to 180°C). Choose based on your solvent’s boiling point.
Condenser Type
Standard Coil Condensers: Suitable for most solvents.
Chiller-Compatible Condensers: Needed for low-boiling solvents like ethanol or ether.
Automation Features
Advanced models offer digital controls for temperature, rotation speed, and vacuum. Automatic lifting mechanisms simplify flask handling.
Safety Features
Look for leak-proof seals, over-temperature protection, and emergency stop buttons.
Budget
Rotovaps range from $500 for basic models to $50,00+ for high-end systems. Balance your needs with long-term reliability.
6. Tips for Maintaining Your Rotovap
To keep your rotovap running smoothly:
Clean flasks and glassware after each use.
Regularly check and replace vacuum pump oil.
Inspect seals and O-rings for wear.
Avoid overheating the bath.
Use compatible solvents to prevent corrosion.
7. Future Trends in Rotary Evaporation
Rotovaps are evolving with new technologies:
Green Chemistry: Energy-efficient models and solvent recovery systems reduce environmental impact.
AI Integration: Smart sensors and software automate processes and optimize settings.
Hybrid Systems: Combining rotovaps with other tools like freeze dryers or reactors.
8. Conclusion: Why Invest in a Quality Rotovap?
A rotary evaporator is more than just a lab gadget—it’s a workhorse for anyone needing precise, efficient, and gentle separation of liquids. Whether you’re developing life-saving drugs, crafting premium essential oils, or analyzing environmental samples, a rotovap saves time, improves safety, and delivers better results.
As a trusted manufacturer of rotary evaporators, we design our systems to meet the needs of labs and industries worldwide. From compact units for startups to heavy-duty machines for large facilities, our rotovaps combine reliability, performance, and ease of use.
Ready to upgrade your lab? Contact us today to find the perfect rotary evaporator for your workflow. Let’s make your liquid separation tasks faster, safer, and more efficient!
About Us
ZZKD is a leading manufacturer and exporter of high-quality rotary evaporators. With 17 years of experience, we serve clients in pharmaceuticals, food science, chemistry, and more. Our products are ISO-certified, backed by a global service network, and tailored to meet your specific needs. Visit website or email contact to learn more!

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
What Is a Rotary Evaporator? Beginner-Friendly Guide to Rotary Evaporation
Learn what a rotary evaporator is, how it works, and how it solves common solvent removal problems in laboratories and production. Clear, beginner-friendly ex...
Read MoreHow Do Rotary Evaporators Work? A Practical, Easy Guide for Faster Solvent Removal
Learn how rotary evaporators work in plain English: vacuum + gentle heating + rotation + condensation. See key specs (2L–50L) and how to choose the right rota...
Read MoreRotovap Distillation | Complete Guide to Rotary Evaporators
Learn everything about rotovap distillation, how rotary evaporators work, applications in chemical labs, and why they are essential for efficient solvent remo...
Read More