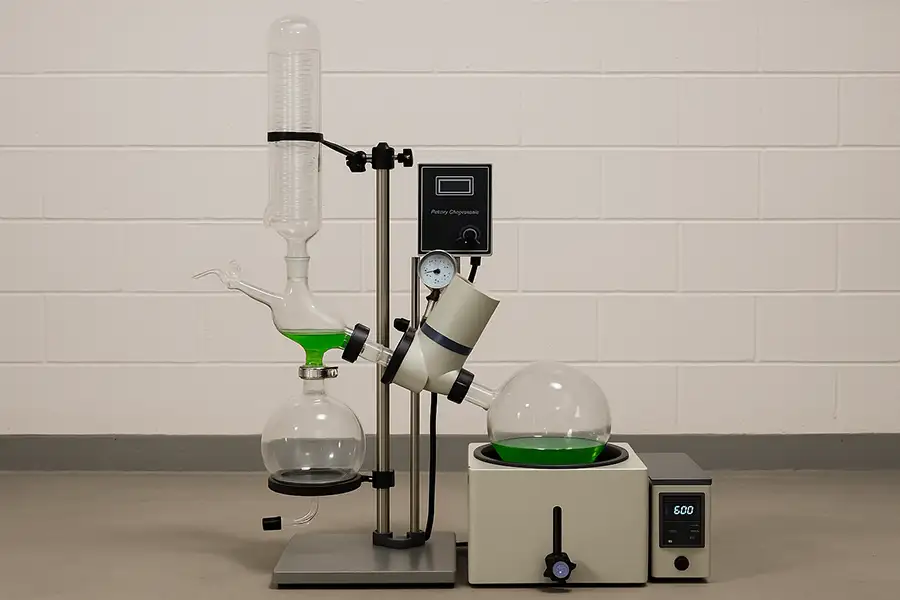
Rotary Evaporator Machine: A Complete Guide
Everything you need to know about rotary evaporators - from working principles to selecting the perfect model for your laboratory or industrial application
What is a Rotary Evaporator Machine?
A rotary evaporator machine is an essential laboratory device used for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. This sophisticated instrument plays a vital role in many scientific domains due to its unique capabilities.
Key characteristics:
Operates under reduced pressure to lower solvent boiling points
Preserves heat-sensitive compounds by using lower temperatures
Uses rotation to enhance evaporation efficiency
Features automated controls for precision processing
Allows solvent recovery for cost efficiency and environmental benefits
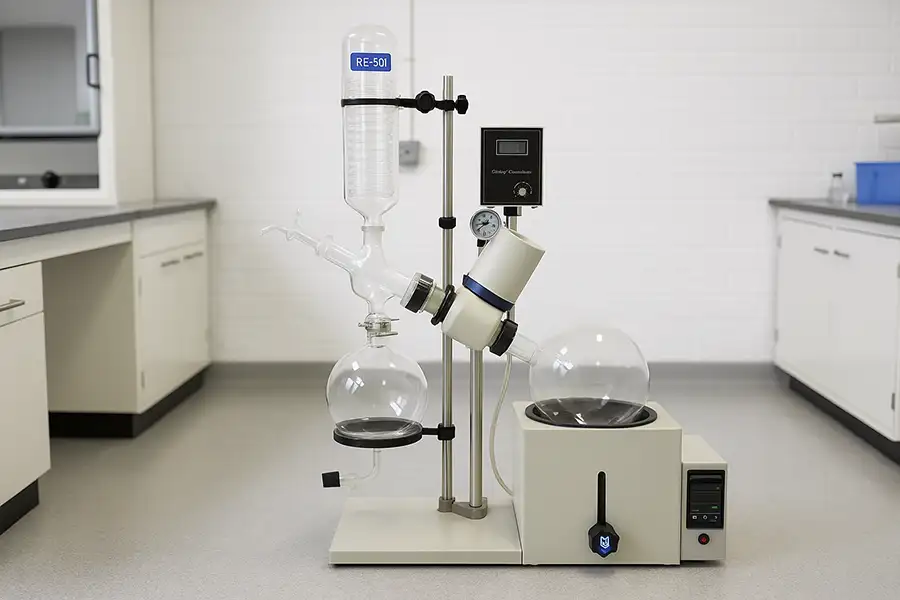

How Does a Rotary Evaporator Work?
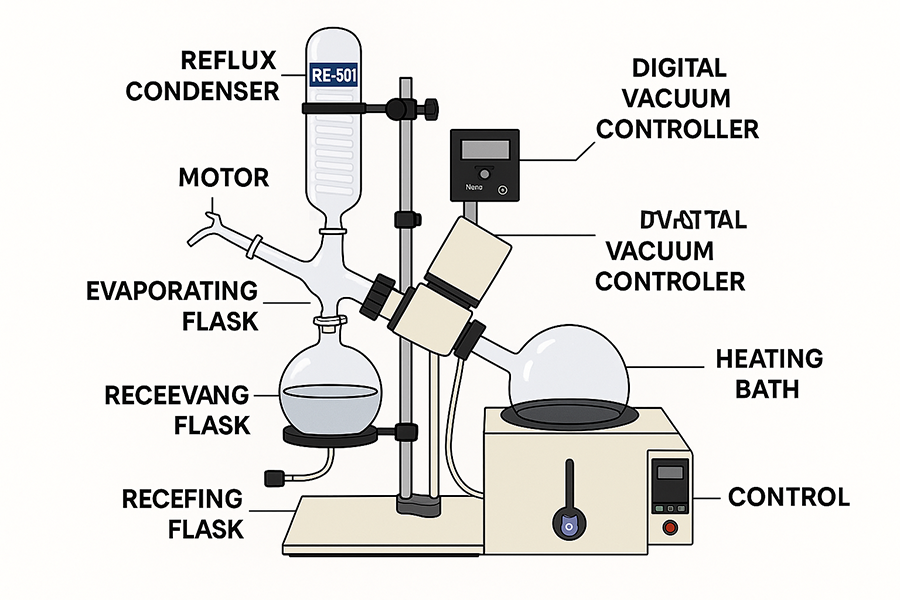
The rotary evaporator consists of several critical components working in harmony:
Motor & Rotation System
Rotates the evaporation flask, increasing surface area and preventing bumping. Rotation speeds typically range from 20-280 RPM.
Heating Bath
Provides controlled thermal energy to the rotating flask (water or oil bath). Temperature control precision to ±0.5°C.
Vacuum System
Lowers pressure to reduce boiling points. Creates vacuum levels from 10-760 mbar depending on application.
Condenser
Cools vapors to liquid state for collection. Various cooling methods (cold finger, coiled, or Dimroth condensers).
Applications of Rotary Evaporator Machines
Rotary evaporators are versatile instruments with applications across numerous industries:
Chemical & Research Labs
Solvent Removal
Compound Purification
Distillation Processes
Sample Concentration
Pharmaceutical Industry
API Extraction
Drug Formulation
Solvent Recycling
Purification Processes
Food & Beverage
Flavor Concentration
Decaffeination
Alcohol Removal
Essential Oil Extraction
Environmental Analysis
Sample Preparation
Solvent Recovery
Waste Treatment
Analytical Concentration
Choosing the Right Rotary Evaporator Machine
Selecting the optimal rotary evaporator requires careful consideration of several factors:
Small-Scale Laboratory
2L Rotary Evaporator
Ideal for:
Research laboratories
Academic institutions
Small batch processing
Budget-conscious setups
Mid-Scale Laboratory
5L Rotary Evaporator
Ideal for:
R&D departments
Pilot plants
Pharmaceutical testing labs
Medium production
Industrial Production
50L Rotary Evaporator
Ideal for:
Large-scale production
Industrial chemical plants
Pharmaceutical manufacturing
Continuous processing
Spatial requirements: Larger units need more lab space and supporting infrastructure
Operating costs: Increased energy consumption and higher solvent requirements
Sample considerations: Larger flask sizes may be inappropriate for valuable samples
Precision: Some processes require smaller setups for better thermal control
Technical Specifications and Comparison
Selecting based on specifications:
| Model | Capacity | Bath Temp Range | Vacuum Level | Typical Batch Size | Rotation Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RE-201D | 2 Liters | RT - 99°C | Up to 399 Pa | 50 ml - 1.5L | 20-280 RPM |
| RE-501 | 5 Liters | RT - 99°C | Up to 399 Pa | 200ml - 4L | 20-250 RPM |
| RE-1050 | 50 Liters | RT - 180°C | Up to 133 Pa | 5L - 45L | 20-200 RPM |

Future Trends in Rotary Evaporation
Current innovations are transforming rotary evaporation technology:
Automated systems: Full process integration with programmable automation
Advanced controls: Touchscreen interfaces with recipe storage
Remote monitoring: IoT connectivity for wireless operation oversight
AI integration: Intelligent systems that learn from historical data
Green technology: Reduced energy designs with higher solvent recovery rates
Modular designs: Configurable systems with swappable components

Complex decision-making in non-standard situations
Equipment troubleshooting and maintenance oversight
Experimental design based on scientific intuition
Ensuring quality control and regulatory compliance
Adapting protocols during experimental anomalies
Conclusion
Rotary evaporator machines form the backbone of countless laboratory processes across research and industry. Their gentle solvent removal capabilities make them invaluable for sample preparation and material purification.
Understanding the fundamental operational principles and carefully matching equipment specifications to your application's requirements ensures optimal performance and value. From compact 2L systems for academic research to industrial-scale 50L units for manufacturing, a well-chosen rotary evaporator delivers exceptional efficiency gains and reproducibility.

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
Explosion Proof Rotary Evaporator - Your Lab's Safety Guardian
Discover why explosion proof rotary evaporators are essential lab safety equipment. Learn how they prevent solvent fires, save costs long-term, and explore mo...
Read MoreEthanol Rotary Evaporator Guide
Discover how ethanol rotary evaporators work, their cost-saving benefits, and how to choose the right model. Learn solvent recovery techniques, safety practic...
Read MoreBenchtop Rotary Evaporator: Your Lab's Solvent-Saving Superhero
Discover how benchtop rotary evaporators revolutionize solvent recovery in labs. Learn space-saving benefits, cost efficiency, and how to choose the perfect m...
Read More


