What Exactly Is a Rotovap Machine and How Can It Help You?
Struggling with solvent removal or sample concentration in your lab? It can be slow and inefficient. This is a common problem many researchers and technicians face daily.
A rotovap machine, or rotary evaporator, is a device used in chemical laboratories for the efficient and gentle removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. It speeds up your work significantly.
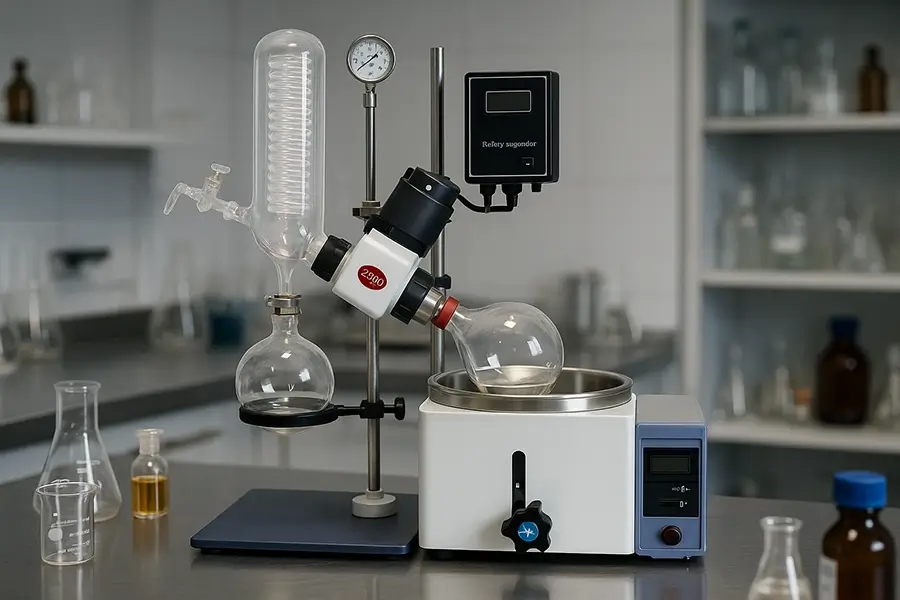

As a manufacturer with over 16 years of experience in exporting laboratory instruments like rotovap machines, I've seen firsthand how vital this equipment is. We've helped countless labs improve their processes. Understanding how a rotovap can fit into your workflow is key. Let's explore this powerful tool further.
How Does a Rotovap Machine Actually Work Its Magic?
Wondering how a rotovap speeds up evaporation without damaging your sample? The process might seem complex, but it's based on some smart scientific principles. It’s a common question we get.
A rotovap machine works by reducing pressure to lower the solvent's boiling point, rotating the sample to increase surface area, and gently heating it. This allows for fast, controlled evaporation.
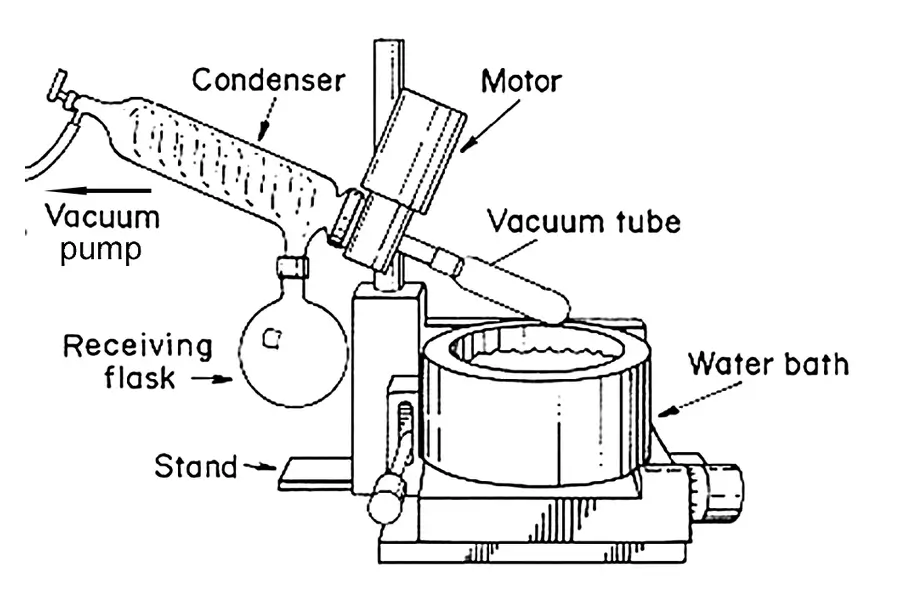
Let's break down the working principle. The magic happens through a combination of three main actions. First, the system uses a vacuum pump. This pump lowers the pressure inside the glassware. When the pressure is lower, liquids boil at lower temperatures. This is great because many samples are heat-sensitive. You don't want to cook your valuable compounds! Second, the evaporation flask, which holds your sample, is rotated. This rotation spreads the sample into a thin film on the inner surface of the flask. A larger surface area means faster evaporation. It also prevents bumping or violent boiling. Third, the flask is partially submerged in a heated water or oil bath. This gentle heating provides the energy needed for the solvent to turn into vapor. The solvent vapor then travels into a condenser. The condenser is cooled, usually with circulating water or a chiller. This causes the vapor to turn back into a liquid, which is collected in a separate flask. The solvent is now separated from your desired compound.
Key Steps in Operation:
Vacuum Application: Reduces the boiling point of the solvent.
Rotation: Increases surface area and ensures even heat distribution.
Heating: Provides energy for evaporation via a controlled temperature bath.
Condensation: Cools the solvent vapor to collect it separately.
From my experience, ensuring a good vacuum seal and stable rotation speed are crucial for efficient operation. We always emphasize these points during training with new users.
What Are the Essential Parts of a Rotovap Machine You Should Know?
New to rotovaps and find the components a bit daunting? Understanding each part helps in operating the machine effectively and troubleshooting any issues that might come up.
The main parts of a rotovap machine include a motor unit for rotation, a vapor duct, a vacuum system, a heated fluid bath, a condenser, and collection flasks.
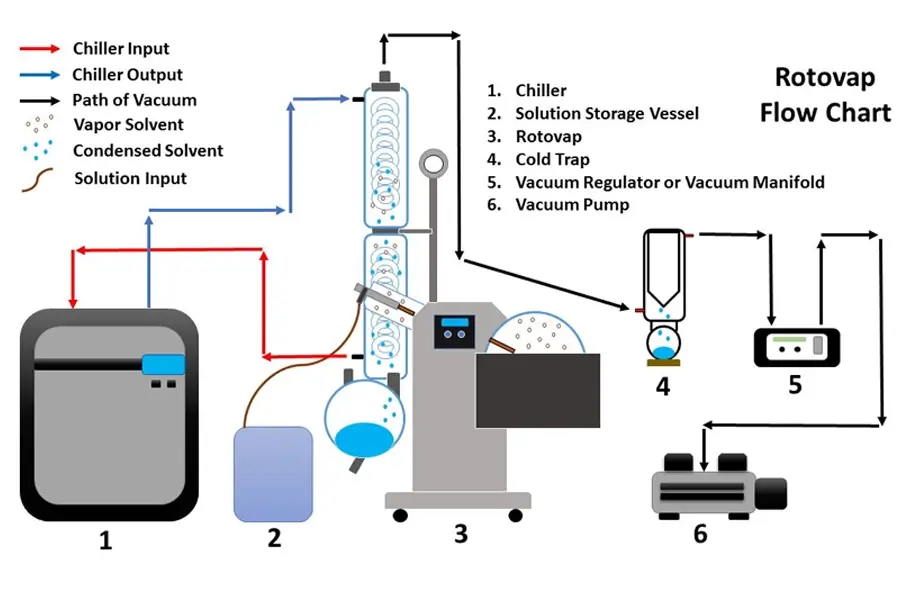
Knowing the components is like knowing the players on a team; each has a specific role. Let's look at them more closely. The motor unit is what rotates the evaporation flask. The speed of rotation is usually adjustable. The vapor duct is the pathway for the solvent vapor. It's also the axis for rotation and connects the evaporation flask to the condenser. A good seal here is very important. The vacuum system, usually an external pump, creates the low-pressure environment. The heated fluid bath (water or oil) gently heats the evaporation flask. Temperature control here is critical. The condenser is a piece of glassware with a cooling coil. Chilled fluid circulates through this coil to condense the solvent vapor. There are different condenser designs, like diagonal or vertical. Finally, there's a condensate-collecting flask to gather the condensed solvent, and of course, the evaporation flask that holds your initial sample. We design our ZZKD rotovaps with user-friendly controls for the motor, bath temperature, and sometimes even an integrated vacuum controller. The quality of the glassware, especially the seals and joints, is something we pay a lot of attention to in our manufacturing process to ensure reliability for our international customers.
Component Breakdown Table:
| Component | Function | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Unit | Rotates the evaporation flask | Adjustable speed, stability |
| Vapor Duct | Passage for vapor, axis of rotation | Seal integrity, material (glass) |
| Vacuum System | Reduces system pressure | Pump capacity, vacuum level |
| Heated Fluid Bath | Heats the sample | Temperature accuracy and range |
| Condenser | Cools and condenses vapor | Cooling efficiency, type (vertical/diagonal) |
| Flasks (Evaporation & Receiving) | Hold sample and collected solvent | Volume, glass quality, joint sizes |
Understanding these parts helps you not only operate the machine but also maintain it and choose the right accessories or spare parts when needed. We always make sure our clients have clear diagrams and support for all components.
Where Can You Typically Use a Rotovap Machine Effectively?
Thinking if a rotovap is right for your specific lab work? These machines are surprisingly versatile and found in many different types of scientific and industrial settings.
Rotovap machines are widely used in chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical research, food and beverage analysis, environmental testing, and cannabis extraction for solvent removal, concentration, and purification.

The applications are really broad. In my 16 years of exporting these machines, I've seen them go into so many diverse fields. For example, in pharmaceutical companies, they are essential for isolating active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) after synthesis or extraction. Researchers use them to concentrate reaction mixtures. In academic universities, chemistry and biology students learn basic separation techniques using rotovaps. They are workhorses in research labs for everyday solvent removal. The food and beverage industry uses them for developing new flavors, extracting essential oils, or concentrating fruit juices. Even in environmental testing labs, rotovaps help in preparing samples by concentrating pollutants from water or soil extracts. More recently, the cannabis and hemp processing industry has become a huge user. They use rotovaps for ethanol recovery after cannabinoid extraction and for purifying extracts. We've customized many units for these specific needs, sometimes larger scale systems. The common thread is the need for gentle, efficient solvent removal. It’s all about isolating what you want from what you don't, without damaging your valuable product. We often discuss specific application needs with our customers to recommend the best configuration.
Examples of Use Cases:
Chemistry Labs: Removing solvents after a reaction, purifying compounds.
Natural Product Research: Isolating active compounds from plant extracts.
Quality Control: Preparing samples for analysis.
Molecular Gastronomy: Creating concentrated flavors and aromas.
How Can You Pick the Perfect Rotovap Machine for Your Lab?
Feeling overwhelmed by the different rotovap models and features available? Choosing the right one ensures it meets your specific needs and gives you the best value for your investment.
To pick the perfect rotovap, consider your sample volume, solvent types, required vacuum level, temperature range, available space, safety features, and budget. Match these to the machine's specifications.

Choosing the right rotovap is a bit like choosing the right car; you need to think about what you'll use it for. First, think about the scale of your work. Are you doing small-scale research with a few milliliters, or pilot-scale work with several liters? This determines the size of the evaporation flask (from 50mL up to 50L or even 100L in our industrial models). Next, what solvents will you be using? Some aggressive solvents might require special seal materials. The boiling points of your solvents will influence the required vacuum level and bath temperature range. For example, high-boiling solvents need a deeper vacuum or higher bath temperatures. Then, consider safety features. Look for things like over-temperature protection for the bath, coated glassware for safety, and easy flask handling. We prioritize these in our CE-certified models. Also, think about automation. Do you need a motorized lift for the bath? Or a digital vacuum controller? These can make operation easier and more precise. Don't forget your lab space and budget. We offer a range from basic, compact models to more advanced systems. I always tell my customers to think about their future needs too. Maybe a slightly larger or more versatile model is a good long-term investment. We are always happy to discuss these factors to help find the best fit from our extensive product line.
Key Selection Criteria:
| Criteria | What to Consider | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Capacity/Flask Size | Volume of samples you process | 1L, 5L, 20L, 50L |
| Solvent Compatibility | Types of solvents (e.g., aggressive, high boiling point) | PTFE seals for chemical resistance |
| Temperature Range | Boiling points of your solvents | Water bath (up to 99°C) or oil bath (higher temps) |
| Vacuum Performance | Required vacuum level for efficient evaporation | Compatibility with available vacuum pumps |
| Safety Features | Operator and sample protection | Coated glassware, over-temp protection, lift type |
| Automation & Control | Ease of use and precision | Digital displays, motorized lift, vacuum control |
What Simple Steps Keep Your Rotovap Machine Running Smoothly?
Want to ensure your rotovap has a long, productive life? Like any lab equipment, a little care and regular maintenance go a long way in keeping it efficient and reliable.
To keep your rotovap running smoothly, regularly clean glassware, check seals and gaskets for wear, ensure the vacuum pump is maintained, and inspect moving parts. This prevents costly downtime.

Maintaining your rotovap isn't complicated, but it's important. Think of it like car maintenance – regular checks keep things in top shape. The first thing is cleaning. Always clean the glassware (evaporation flask, receiving flask, condenser) after each use, especially if you're working with different samples. Residue can build up and affect performance or contaminate future experiments. Next, pay attention to the seals and gaskets. These are usually made of materials like PTFE. They ensure a good vacuum seal. Over time, they can wear out or get damaged, especially with certain chemicals. Check them regularly for cracks or loss of elasticity and replace them if needed. We always stock spare seals. The vacuum pump itself needs its own maintenance, like oil changes if it's an oil pump. A healthy pump means a good vacuum for your rotovap. Also, check any moving parts, like the rotation mechanism, for smooth operation. Keep the heated bath clean and ensure the temperature sensor is working correctly. For the condenser, make sure the cooling lines are clear and there are no leaks. As a manufacturer providing a one-year warranty and lifetime cost-price service, we always advise our customers on these simple steps. Following a basic maintenance schedule can save a lot of headaches and keep your experiments running smoothly for years. It's an investment in reliability.
Basic Maintenance Checklist:
Daily/After Use: Clean all glassware thoroughly. Empty and clean the collection flask.
Weekly: Inspect vacuum seals and gaskets for wear or damage. Check vacuum tubing for cracks.
Monthly: Check the water/oil level in the heating bath. Inspect the motor and rotation mechanism.
As Needed: Perform maintenance on the vacuum pump as per its manual. Replace worn seals or gaskets.
We find that labs that implement a simple routine like this experience far fewer interruptions and get more consistent results from their rotovap machines.
Conclusion
A rotovap machine is a key lab tool for efficient solvent removal. Understanding its function, parts, uses, selection, and care helps you maximize its benefits in your work.

E-mail:
WhatsApp:
Address:
19/F, Block B, Guohong Mansion, Hi-Tech Development Zone, Zhengzhou City, Henan Province, China
Related blogs
You May also like
Rotary Evaporator Machine - Complete Guide
Comprehensive guide to rotary evaporator machines covering working principles, components, applications, technical specs, and tips for selecting the right mod...
Read MoreExplosion Proof Rotary Evaporator - Your Lab's Safety Guardian
Discover why explosion proof rotary evaporators are essential lab safety equipment. Learn how they prevent solvent fires, save costs long-term, and explore mo...
Read MoreEthanol Rotary Evaporator Guide
Discover how ethanol rotary evaporators work, their cost-saving benefits, and how to choose the right model. Learn solvent recovery techniques, safety practic...
Read More


